Fluorescence based cadmium detection by protein-assisted synthesis of quantum dots
It is worth doing internships and master's theses in our team! One of these internships resulted in a joint publication on the detection of cadmium ions in water.
M. Misiak, K. Jamicka, A. Bednarkiewicz, Fluorescence based cadmium detection by protein-assisted synthesis of quantum dots, J Lumin 281 (2025) 121176. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JLUMIN.2025.121176.
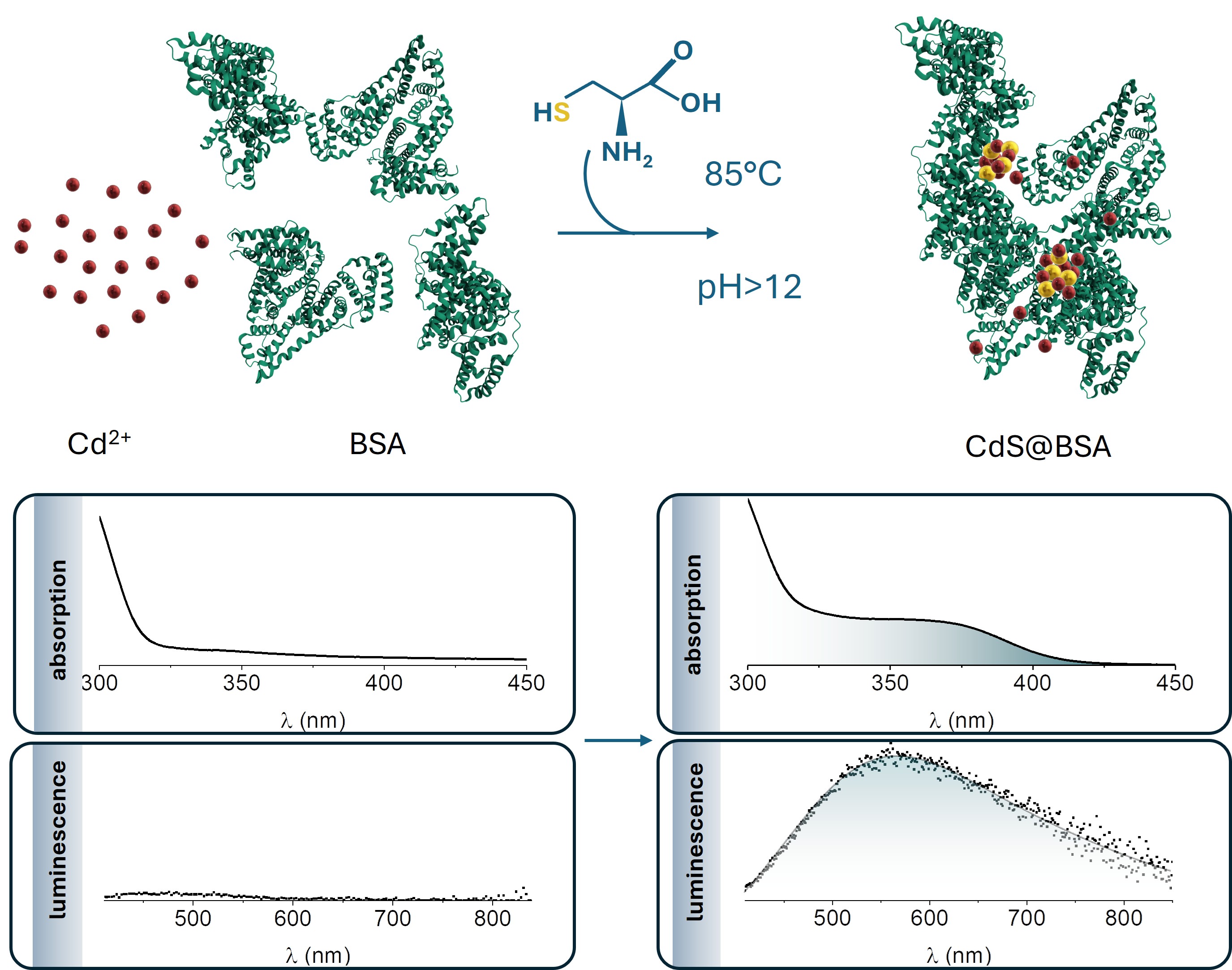
Abstract
The development of an accessible and cost-effective method for heavy metal ions detection holds immense potential for addressing challenges related to detection of contamination in the context of environmental and public health issues. Here, we present an inexpensive and facile method to detect cadmium ions, utilizing bio-assisted synthesis of Cd-containing fluorescent quantum dots. The synthesis is mediated by proteins, which serve as both templates and stabilizers during the formation of the nanoparticles, and enable the control of their size and thus their optical properties. The proposed method demonstrated a detection limit of 0.2 μmol/mL for cadmium ions in water. These studies represent the first attempt at utilizing this approach for selective detection of cadmium ions, paving the way for further innovative solutions in affordable heavy metal ions sensing. The findings may stimulate further investigations of alternative applications of material formation techniques, potentially leading to development of novel applications beyond traditional realms.